Abstract
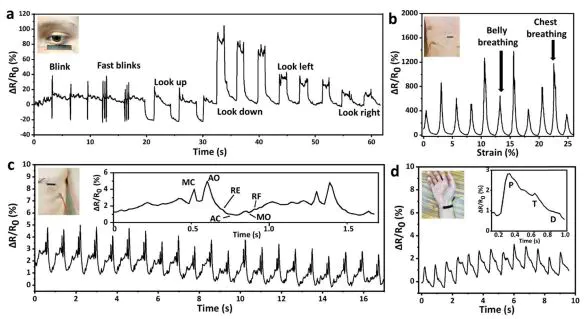
This study aimed to explore lignin as a naturally occurring aromatic precursor for the synthesis of LIG and further fabrication of ultrasensitive strain sensors for the detection of small deformations. One-step direct laser writing (DLW) induced high quality porous graphene, so called laser induced graphene (LIG), from kraft lignin under the conditions optimized for laser power, focus distance, and lignin loading. An electrode based on the resulting LIG was facilely fabricated by transferring LIG onto an elastomeric substrate (i.e., Dragon Skint). The novel LIG transfer was facilitated by spin coating followed by water lifting, leading to the full retention of porous graphene onto the elastomeric substrate. The strain sensor was shown to be highly sensitive to small human body motions and tiny deformations caused by vibrations. It had a working range of up to 14% strain with a gauge factor of 960 and showed high stability as evidenced by repetitive signals over 10 000 cycles at 4% strain. The sensor was also successfully demonstrated for detecting human speaking, breath, seismocardiography (SCG), and movement of pulse and eye. Overall, the lignin-derived LIG can serve as excellent piezoresistive materials for wearable, stretchable, and ultrasensitive strain sensors with applications in human body motion monitoring and sound-related applications
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code, math, and images.