Channel-Coupling Fano Resonance and Acoustic Metadamping
Abstract
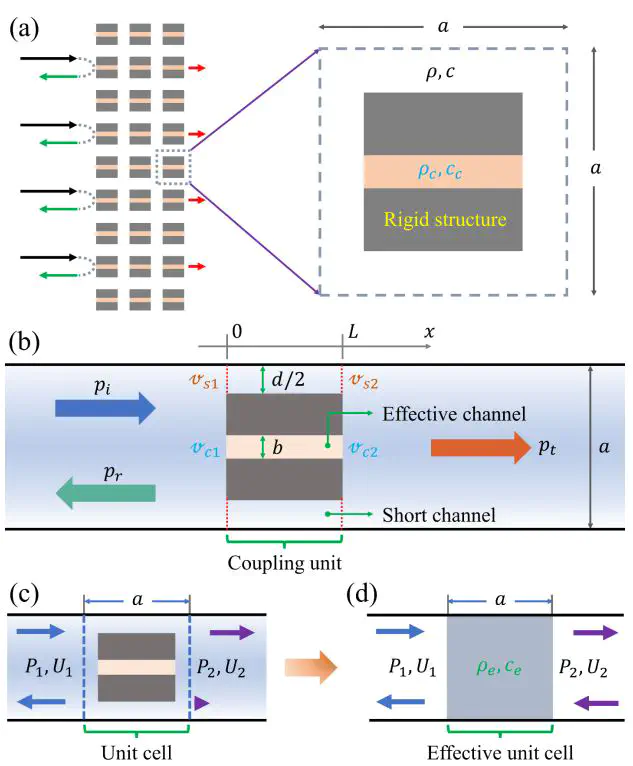
Fano resonance featuring asymmetric spectral profiles originates from the interference of local resonances and background continuum. Its narrow-band nature looks seemingly adverse to broadband noise cancellation purposes. In this study, we report theoretically on an intriguing acoustic metamaterial capable of generating multiple Fano-like resonances to realize a broadband sound barrier with satisfactory transmission loss performance. Our proposed design involves an effective channel characterized by effective parameters and short channels filled with air. The effective channel support both monopolar and dipolar modes which interact with the continuum state admitted by the short channels to generate a pair of Fano-like resonances. Due to the destructive interference of sound waves, the two resonances result in transmission loss overall exceeding 10 dB over a broad range 0.6-1.1 kHz. In order to further optimize the overall performance, we introduce metadamping by integrating additional viscous foams in the proposed unit cell. Furthermore, for future experimental tests, the dampened design is decoded into a real space-coiling cell which exhibits identical functionality and is assembled into a partition wall to ensure transmission loss over 10 dB across the range 0.32-4 Hz. Lastly, acoustic negative refraction is accessible by deploying two coupled space-coiling channels in a similar fashion. We believe this work paves the way for realizing effective broadband sound insulation devices with efficient ventilation.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code, math, and images.